Learn Swimming In Singapore: The Definitive Guide 2019
Swimming is an important life skill and the only sport that can save you and others life
It is no secret that learning how to swim is one of the most important skills to have for survival and the betterment of health!
Swimming has been practiced as both a sport and as a leisure recreational activity for many thousands of years.
Reaching the proficiency of great swimming is one culmination of many swimming techniques: you need to master floating, manipulation of water, freestyle swimming, backstroke, breast-strokes, butterfly swimming, turnings, starting, diving techniques, survival in open water and survival swimming. It might seems effortless for people who have reached the highest level of swimming and competition.
For beginner or novice, on the other hand, seems like an exhausting chore that can be done well with people who have a natural talent for it. This guide will help you to learn swimming with instructors, how to learn swimming step by step and how to learn swimming by yourself.
Bottom line?
If you want success in swimming, you need to follow a systematic building of solid foundations of skills and techniques with enough reading, following instructions through swimming lessons and many hours of practice.
Don’t have time to read the whole guide right now?
No worries. Let me send you a copy so you can read it when it’s convenient for you. Just let me know where to send it.

Swimming Fundamentals
Swimming Pools

Swimming Apparels

Training Equipment

Floating

Water Manipulation

Freestyle Swimming Techniques

Backstroke Swimming Techniques

Breaststroke Swimming Techniques

Butterfly Swimming Techniques
Chapter 1: How to learn swimming by yourself and fundamentals
Swimming can be defined as simply the act of knowing how to propel oneself through the water.
Last year we have done research on the best way to guide children to know how to swim. Research shows that weekly swimming lessons and intensive programs seem to be the most cost-effective and the most effective ways to pick up swimming.
The facts: Swimming differs from other sports in many different ways. Swimming is not a natural activity for human beings. Humans bear little resemblance to species that are geared to operate in the aquatic environment.
Humans do not have gills in order to swim thus humans have to make certain adaptations- in part to accommodate the differences and also to take advantage of them.
For swimming success, you must first become accustomed and comfortable in the aquatic environment which differs quite dramatically from a land-based environment that we typically operate on a daily basis.
#1: How to learn swimming and why is swimming so different from the other land-based sports?
Humans operate on a daily basis in a land-based environment. Understanding the key differences between humans and aquatic creatures will help us easier in identifying the differences.
As most terrestrial creatures, we walk upright and the natural position for most of our waking hours is basically vertical. In the water, however, most of what we do involves being horizontal, and these differences will take some time for people to get used to for most people.
Most sports, success depends largely on strength and speed. In swimming, however, there is nothing solid to push against, thus though strength matters in swimming, it will much more crucial to be able to know how to apply pressure to the water in the correct way.
Water is naturally fluid; it moves around you rather than resolute resisting you in the way a solid does. Similarly, the speed in swimming comes not necessarily from how fast you move your body parts but rather using the movements to put pressure on the water in an effective way.

Chapter 2: Swimming Pools
Before diving into swimming pools, it’s good to know what are the different types and sizes of swimming pools available.

Why is this important?
Knowing all these various configurations will help to prepare us better know where to go for better learning and training.
When it comes to swimming, there are 2 kinds of swimming pools you can see readily:
#1: LCM- Long Course Meter Pool
Long course meter pool is often referred to as the Olympic-Size pool. LCM Pools are 50 meters long.
#2: SCM- Short Course Meter Pool
A short course meter pool is often referred to as the Training Pool. SCM pools are 25 meters long.

#3: Competition Pools
Olympic-size pools also known as competition pools share certain standard features such as starting blocks, set of backstroke flags.
Flags or pennants are strung across the pool’s lanes 5 meters from the edge of the swimming pool to signal backstroke swimmers that they are approaching a wall – crucial safety feature.
Competition pools are also outfitted with starting blocks or platforms. During competitions, a thin sensor will be attached to pool walls to record the timings of each swimmer’s first touch.
#4: Pool Races
Every national swimming federation has its own unique minor rule variations, the majority of swimming meets and races take place in the pools rather than in open water environments.
Swimming venues around the world organize varying events featuring various strokes and distances but all competitors start at the same time and adhere to the same rules of the prescribed stroke, the finish order is ranked from the fastest to the lowest. “Similar” swimmers are categorized and put to swim together via “heats” events and timed with the fastest swimmers declared as the winner.
CHAPTER 3: Swimming Apparels
It is no secret that learning and practicing swimming is the effective ways to pick up the sport of swimming and preparing yourself for the competition.
But here is the deal:
Choosing the right suit is an important part of appreciation of swimming and providing comfort in the water.
Swimsuits differ and unlike the ones you wear to the beach is not necessarily the best choice for swimming workout. Swimsuits provide maximized fit and functionality.

#1: Swimsuits
Male Swimwear
- Brief
- “Jammer” which runs from waist to just above the knee made of material of nylon, spandex, polyester or combination.

Female Swimwear
- One-piece suit covering the body from the mid-thighs to the shoulder in varying style and cut.
- Bikini better known as the two-piece swimsuits.
Training purposes
Swimmers may opt for less expensive, less restrictive providing some extra elements for training purposes such as the increased drag of looser suits.
#2: Goggles
Goggles come in all kinds and shapes from snorkeling, scuba diving ones to the ones used in triathlon. When it comes to selecting and purchasing of goggles, quality assessment should be on the basis not of the price but of the fit. The best goggles are the ones that fit you and fit your face.
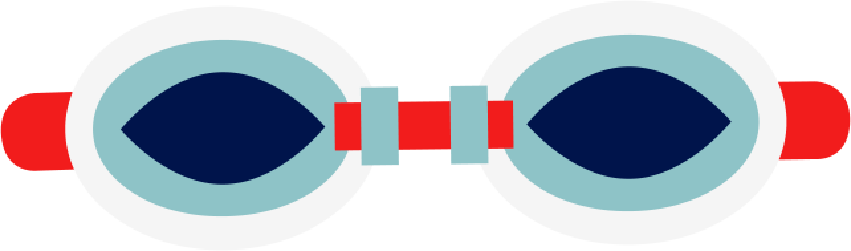
Testing the goggles fit
- Place the eyepieces on your eye sockets, below the bony part where the eyebrows are located, in the softer part of each socket.
- Without using the strap, press the goggles gently on the soft tissue and see if they stay even for just a few seconds.
- If they do, Cheers~ you have got the good fit!
#3: Caps
Swimmers with long hair usually wears a cap:
- To keep the hair out of the way and reduces the drag
- Provides a measure of protection from the sometimes harsh chemicals
- Provide a measure of protection from environment factors
Bad environmental factors for wearing caps as a measure:
- Outside sun and UV factors
- Bacteria in the water
- Chemical in the water such as residual like suntan lotion came off other swimmers
- Runoff from chemicals on the deck during rain
- Chemical from pollution that can be found in open water environments
Materials in the making of swim caps:
- Latex
- Silicone
- Neoprene for those swimmers in cold weather
Always keep in mind that swimming caps are like rubber bands and can stretch and break, do take care of it and follow the care-and-use guide in the packaging.
CHAPTER 4: Training equipment
4 Reasons to use training equipment
- Conduct drills
- Improve swimming specific movements by increasing the resistance
- Assistive device to enable swimmers to isolate a specific movement or set of skills
- Make many skills and drills mastery easier

#1: Kickboards
- A kind of equipment made of some foam to provide flotation
- Its purpose is to provide a buoyancy assistance that swimmers can isolate and train the kicking motion.
- Used to train all 4 competitive strokes
#2: Fins
Fins commonly used in swim training to add resistance to kicking motion, helps people to swim more easily or to make the workout harder.
Fins come in many shapes and sizes, examples of some of the fins are monofins and the breaststroke fins.
#3: Paddles
Like goggles and fins, paddles come in a variety of shapes and sizes as well. They are often used to create extra resistance by increasing surface areas of the hands. Novice swimmers are advised to use smaller paddles to minimize the risk of injury.
#4: Pull buoys
Pull buoys are used for isolation and training for certain techniques. Usually fitted in between the thighs just above the knees and the swimmer will keep it in place by squeezing the thighs together. This kind of arrangement will prevent the swimmer from using any effective kicks in freestyle or backstroke thus train the pulling motion of the swimming arm stroke.
#5: Snorkel
Snorkel is designed for swimmers to focus fully on their strokes without the added concern of when and where to breathe.
Standard swimmers’ snorkels are typically center-mounted rather than offset like they are going for scuba diving, with a strap that will go around the head.

CHAPTER 5: Floating
Floating with support
Floating involves the ability to stay suspended in the water in a relatively horizontal position (on the front or on the back) with minimal to no movement.
The most basic way to float is to extend all appendages outward to lift the feet off the bottom of the pool. Your support of the student should mainly of supporting the torso and head.
One great way to do it is by supporting swimmers floating on his back and have the swimmer rest his or her head on the instructor or friend’s shoulder.
Maintain this few cues if you are training alone, with an instructor or friends.
Back float cues:
- Head back
- Ears remain in water
- Chin-up
- Arms and legs out
- Belly up
Front float cues:
- Nose towards the floor
- Arms and legs spreading outwards
- Belly down
Differentiation exercises with instructor/friends:
- Provide support under the back and head; you may use several pool noodles and have them remove one at a time as you/the student progresses.
- Provide flotation support under a body part that is denser than others.
- Hold floating barbells in each hand or under each armpit for support.
- Inexpensive blowup rafts somewhat deflated for support.

CHAPTER 6: Water manipulation
Moving in water without generating propulsion forward or backward is known as stationary propulsion (treading water).
You need to master this technique through practice to effectively manipulate the water. The skill of keeping the head above the water while remaining in one place is essential for safety and helps students feel confident and comfortable in the aquatic environment.

CHAPTER 7: Freestyle swimming techniques
The front crawl is fast and the most efficient stroke of all. The streamline position and continuous propulsion created from the leg and action at large causes it to be the fastest.
The sequence alternating actions of the arms and legs is good to the joints and full stroke helps develop cardio capacity faster than any other strokes.



